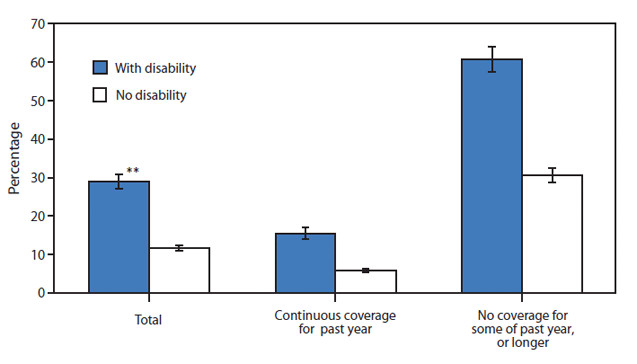
* Based on responses to two questions: "During the past 12 months, has [person] delayed seeking medical care because of worry about the cost?" and "During the past 12 months, was there any time when [person] needed medical care but did not get it because [person] could not afford it?" Both questions exclude dental care.
† Estimates are age adjusted to the 2000 U.S. census civilian, noninstitutionalized population.
§ Disability is any difficulty in basic actions, which includes movement, vision, hearing, emotion, and cognition. Of 188,273,000 working age adults, 24.5% reported a difficulty in basic actions.
¶ Insurance coverage includes public and private plans and is stratified by duration of coverage during the year before the interview.
** 95% confidence interval.
 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir