FIGURE 3. Percentage* distribution of gestational ages at time of abortion, by age group of women — selected states,† United States, 2009
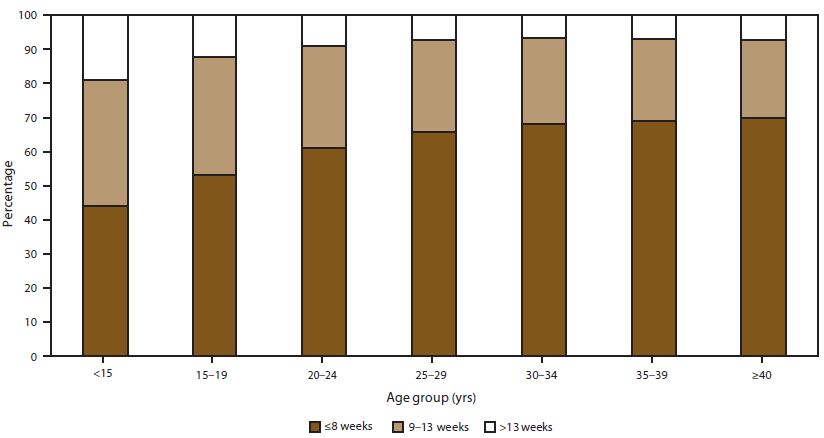
* Based on the total number of abortions reported with known weeks of gestation.
† Data from 38 reporting areas; excludes California, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Illinois, Kentucky, Maryland, Massachusetts, Nebraska, New Hampshire, Pennsylvania, Vermont, Wisconsin, and Wyoming.
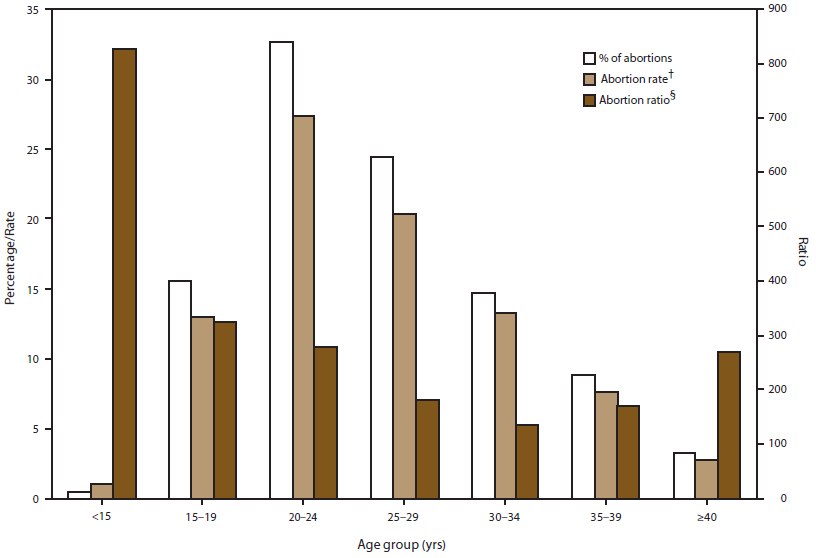
Alternate Text: This figure is a bar graph that displays data from 45 reporting areas (excluding California, Delaware, Florida, Maryland, New Hampshire, Vermont, and Wyoming) for 2009 showing the abortion rate (i.e., the number of abortions per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years, the abortion ratio (i.e., the number of abortions per 1,000 live births), and the percentage of total abortions by the age group of women who obtained a legal abortion in the United States in 2009. Women aged 20-29 years accounted for the majority (57.1%) of abortions and had the highest abortion rates (27.4 and 20.4 abortions per 1,000 women aged 20-24 and 25-29 years, respectively). Women in the youngest and oldest age groups (aged <15 or ≥40 years) accounted for the smallest percentage of abortions (0.5% and 3.3%, respectively) and had the lowest abortion rates (1.1 and 2.7 abortions per 1,000 women aged <15 and ≥40 years, respectively).
 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir